Abrasive Jet Machining is useful for delicate finishing operations. It is used for removing thin metal particles from hard and brittle parts. With Abrasive Jet Machining, you can machine those intricate areas where the conventional Machining process can not reach. That is why Abrasive Jet Machining comes under the un-conventional Machining process.
Let’s learn in this article more about Abrasive Jet Machining, its advantages, disadvantages, and its applications.
What is Abrasive Jet Machining
As the name suggests, Abrasive Jet Machining uses a jet of abrasives to remove materials from the workpiece. Abrasive Jet Machining is also known as Abrasive micro blasting, Pencil blasting, or Micro Abrasive Blasting.
Abrasive Jet Machining is useful to form edge shapes or surface machining in hard, brittle, and temperature-sensitive material. Commonly used Abrasives are aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or glass beads. The size of abrasive particles is usually .001 inches.
The jet is formed by natural air or nitrogen gas. The pressure in the abrasive and the gas mixture is about 170-900 KPa. The velocity of the jet is usually 1000km/hour.
Abrasive Jet Machining Working Principle
Abrasive Jet Machining could able to remove metals due to the erosion of high-speed abrasive particles. As I said before that the velocity of the jet is about 1000 km/hr. So with this velocity, when abrasive hits the surface of the workpiece, the workpiece particles get loose.
When there are continuous impacts of the high-speed jet, those loose particles from the workpiece get flown away.
Here is a schematic diagram of abrasive jet Machining process.
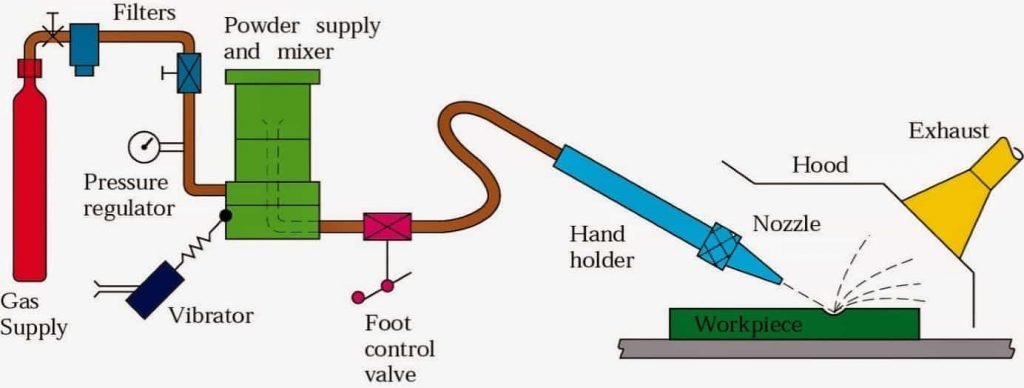
As you can see, there is a mixing chamber where the high-speed air or gas mixes with abrasive particles. A regulator regulates the flow of gas. A filter is used to remove any foreign particles from the gas.
The filtered gas gets into the mixing chamber at a pressure of 3-8 Kgf/cm 2, and when it enters the chamber, the chamber is already vibrating at 50-60 Hz.
The mixture then flows through the connecting hose at a speed of about 1000 km/ hour and hits the workpiece surface through the nozzle. Due to repeated high-speed abrasive impact, metals from the surface of the workpiece get removed.
The feed rate of abrasive can be controlled by the aplitude of vibration of mixing chamber.
The material removal rate depends on the following factor.
- The velocity of the jet
- Abrasive particles size
- The pressure of the mixture
- The material composition of the workpiece
- Nozzle diameter
- The angle of attack of the jet
- The distance between nozzle and workpiece
Key parts of Abrasive jet machine
Here are few key parts of a typical abrasive jet machine.
- Gas supply unit
- Gas filter
- Pressure Gauge
- Regulator
- Mixing chamber
- Connecting hose
- Nozzle
Gas supply unit
The gas supply unit supplies the pressurized gas. Usually natural air or nitrogen gas is used.
Gas filter
The gas filter removed any foreign particles from the gas. If there are any impurities in the gas, it may affect the machining process and may cause some damage to the workpiece surface.
Pressure Gauge
Pressure gauge controls the pressure and indicate at what pressure the gas is flowing into the mixing chamber.
Regulator
Regulators control the amount of gas that is getting into the mixing chamber. As we all know, the gas’s pressure and velocity play a big role in the machining process, so regulators control that flows rate.
Mixing chamber
Mixing chamber is the place where the gas and abrasive particles meet.
Connecting hose
After the mixing chamber, the gas and the abrasive mixture goes through the connecting hose to reach to the nozzle inlet.
Nozzle
The nozzle is the part that sprays the abrasive mixture on the workpiece surface. The inlet of the nozzle is a divergent shape, and outlets are convergent. The diameter of the outlet is usually between .2 to 1 mm.
Nozzles should be abrasive resistant, otherwise, the nozzle will get damaged by abrasive particles. That is why nozzles are made of tungsten carbide or synthetic sapphire.
Tungsten carbide nozzle has a life of about 12-30 hours and synthetic sapphire nozzle has a life of about 400 hours .
The nozzle can be handheld or can be mounted on a fixture for automated operation.
Application of Abrasive Jet Machining
- Machining of forged parts
- Polishing or machining of plastic molded parts
- Making intricate cuts or polish
- Frosting of the interior surface of glass tubes.
- Producing different shapes in parts where traditional machines can not reach
- Machining of parts made with temperature-sensitive material.
Advantages of Abrasive Jet Machining
- No heat source required
- Heat sensitive metals can be machined
- Can create shapes or machine those surfaces where other traditional machines can not reach
- The surface finish obtained is very smooth
- Low equipment cost
- A skilled technician is not required.
- Fragile components can be machined.
Disadvantages of Abrasive Jet Machining
- The very slow material removal rate
- Additional cleaning of the machined surface is required.
- Nozzle needs to change very often as those wears quickly
- Poor machining accuracy
Conclusion : Abrasive Jet Machining
That’s all I have in this article. I hope you all got a fair idea about abrasive jet machining through this article. I can understand that this article offered just a basic introduction to this process. As and when you work on the process, you may be able to gain more knowledge. But as a mechanical engineer, you should have the basic knowledge of this process, and that’s what I offered here.
If you still have any question for have any queries then please do write in the comment section and I will be happy to respond.
You may also like to read: What is a CNC machine



