The construction industry is one of the most booming business sectors across the globe. With the exponential expansion of urban environments, the requirement for more buildings/structures is only increasing.
A construction site uses a lot of different processes to execute the end product, including welding. In this blog, the importance of having a planned welding process, its applications and benefits in construction, and four common types of welding procedures will be discussed.
What is a Welding Procedure Specification?
Welding seems cut and dry at the outset, but it can have several complications. Despite the expertise of the craftsmen, a weld can be subpar for a particular structure.
This calls for a standard procedure or protocol that welders can implement on construction sites, known as welding procedure specification.
In essence, it is a list of rules and procedures to follow to execute a particular weld that meets local ordinances. This can include mentioning the type of material, the type of weld to follow, the exact procedure, and the ideal outcome.
Therefore, by following a welding procedure specification, one can take the guesswork out of the equation, creating high-quality, sturdy welds, a necessity in the construction industry.
Hence, before implementing any welding process, a company must have a WPS on hand that meets the region’s quality and safety standards.
Welding Applications for Construction Industry
There are numerous applications of welding in the construction industry. A few are listed out below
- To create structural frameworks using metals. These frameworks are the backbone of any structure, hence the welding has to be perfect and incredibly strong.
- It is also used to connect various structural components such as I-beams, trusses, and columns, which act as main supports for the building.
- Apart from structural uses, welding also finds use in smaller construction projects such as installing handrails, foot joists, stairs, and more.
- Lastly, they are also applied in electrical systems to create wire conduits, plumbing systems to install water pipes, ventilation systems to install air vents, and fuel systems to install pipes that transport gas.
With some clarity on applications, it’s time to examine the major benefits of welding in the construction industry.
Benefits of welding in the Construction Industry
Durability
As mentioned above, welding is used in structural frameworks. Weighing thousands of tons, there is incredible stress on these metal beams, and failure can result in a major collapse.
Fortunately, with sound welding processes and techniques, it is not an issue, and such incredible structures are conceived and engineered in a very short time.
Efficiency
The construction industry makes a huge profit mainly due to its high productivity rate. Welding enables and improves this efficiency with technology such as ArcReach, which provides a constant power source irrespective of distance, automation equipment, and multiprocess welders, wherein different welds can be carried out in a single machine.
Versatility
Welding can be implemented in almost any type of construction process. Be it welding huge structural beams or the smallest of pipes or electrical conduits, it can all be done with one process.
Economical
While welding is economic in itself due to its efficiency, the benefits can be expounded by renting out high-quality equipment for construction contract projects.
4 types of welding procedures on construction sites
1. ARC/SMAW Welding
One of the most common types of welding, arc welding is also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding. It is a form of welding wherein the electrode is a stick through which electric current passes. When this charged stick is applied to the area to be welded, it creates a high-temperature arc between the stick and metal surface, thereby creating the weld.
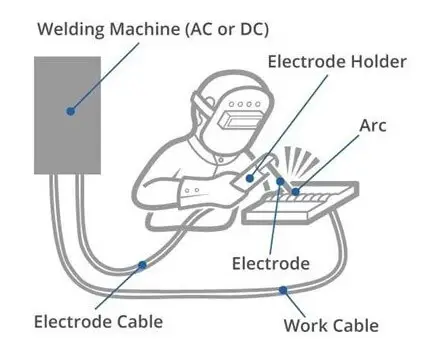
The electrode eventually melts into the metal creating a flux, which shields the weld from contamination and oxidation. As is evident, this is a majorly manual process but is easy to master. It is also inaccurate, as it can create spatters, requiring polishing or cleaning up once the weld is completed.
Despite being a manual process, it is quite easy to maneuver and can be performed outside in harsh weather conditions. Hence, it is used in construction to fabricate steel and industrial-grade iron.
2. TIG/GTAW Welding
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) or Gas Tungsten Arc Gas Welding (GTAW) is one of the most complicated yet versatile welding methods used in construction. It primarily consists of a non-consumable tungsten electrode. When this electrode comes in contact with the metal surface, an arc is created. The process also uses argon gas to shield the weld from oxidation.
The major challenge in TIG welding is using two hands to perfect the process. A welder must use a TIG torch with one hand to heat the metal and another hand to feed the electrode to create the arc.
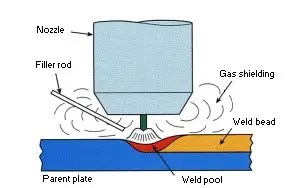
Moreover, the heat also needs to be controlled manually, generally with the help of a foot pedal. This complicated process also allows for better accuracy as the technician can precisely control the heat required for a particular section.
This leads to accurate welds with no slag formation. Lastly, TIG welding is ideal for multiple materials such as brass, copper, magnesium, bronze, stainless steel, aluminum, steel, nickel alloys, and more.
3. MIG/GMAW Welding
Metal Inert Gas or Gas Metal Arc Welding, is also a popular welding method used in construction as well as everyday household projects. Unlike TIG welding, the process here is straightforward.
A MIG welder comprises a holder with a filler material or electrode, which also has shielding gas coated onto it. When electricity is fed to the electrode through a constant power source, it creates an arc by coming into contact with the metal surface. The gas coated on the electrode prevents contamination.
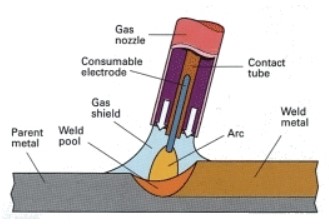
One of the biggest advantages of MIG welding is the ease of use. With a non-expendable electrode, MIG welders can be used continuously to create highly accurate welds with minimal spatter.
This feature allows for automation, making it a major benefit in construction projects. Conversely, MIG welding is not advisable outdoors, as it is susceptible to rain, winds, and dust. Hence, its use in fabrication in the construction industry is highly dependent on the task.
4. FCA/FCAW Welders
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), has similarities to both MIG welding and arc welding. Like MIG welding, FCA welders require a constant power source to carry out the process.
Hence, multi-welder machines can typically perform MIG and FCAW with a single piece of equipment. Moreover, like arc welding, FCAW doesn’t require a shielding gas. Although, it doesn’t use a stick electrode either. It uses a consumable wire or electrode in its core that acts as a flux, simultaneously creating a shielding gas as the weld is performed.
Hard to perform and master, FCAW is perfect for fabricating or repairing thick metals, making it a staple in bridge construction and shipbuilding industries. Perfect for complex welding operations, it is a staple in construction sites for residential non-residential structures.
The only drawback with this type of welding is the formation of slag/residue, but it can be easily cleaned up with a wire brush or polisher.
Conclusion: Types Of Welding Procedures
Overall, all these 4 types of welding methods are used extensively on construction sites. However, before using any of these techniques, it’s important to create welding procedure specifications as per local laws and building codes to ensure optimal safety standards.
You may also like to read: Types Of Welding Defects
This is a guest post By Dhruv

Dhruv Mehta is a Digital Marketing Professional who works as a brand consultant and provides solutions in the digital era. In his free time, he loves to write about manufacturing, finance & home decor. Follow him on Twitter or connect with him via LinkedIn.



