When it comes to charging EV vehicles, there are two different types of charging facilities available in the market: DC charging and AC charging.
If you are confused between AC Vs DC chargers for your EV, this article is for you.
While at home, we mostly use AC charging, but we use DC charging at fast charging kiosks.
There is a significant difference between AC Charging Vs DC Charging, and in this article, we will try to understand those differences.
Before we discuss the differences between AC and DC charging, we need to understand what AC and DC are.
How do both types of charging affect the batteries? Which charging method is faster? This article will explain all these.
What Is AC Current?
AC means alternating current. An alternating current is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time.
The waveform of alternating current is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with the positive direction of the current and vice versa.
The beauty of AC is that the voltage can be reduced or amplified using a step-up or a step-down transformer. Thus, it is easy to transport AC from the power plant to the grid and from the grid to the household.
We use AC in the household, but most of our appliances and gadgets use only DC. The charger through which we charge our cellphones, appliances, or gadgets converts the AC to DC and feeds it to the device. So, basically, those chargers are AC-to-DC converters.

What Is DC Current
DC always moves in a straight line in the waveform graph. It is usually generated from renewable energy sources like solar panels.
DC power can be converted to AC power using a rectifier. A converter is used to convert the AC power to DC power. For EV fast charging stations, High-Voltage DC (HVDC) is used, where the voltage range is between 400V and 1000V.

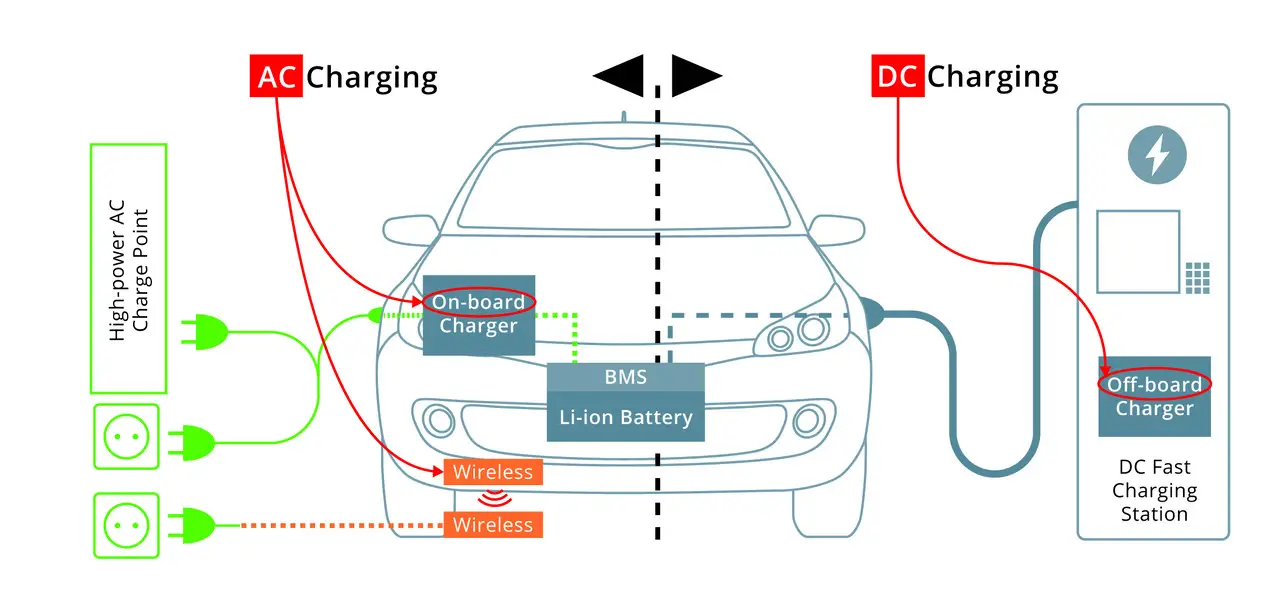
AC Charging Vs DC Charging For Electric Vehicles
If you are confused between AC Vs DC charging for your EV, then do you know that electric vehicle batteries can only take DC?
Most electric vehicles have an inbuilt converter to convert AC to DC.
When you charge EVs at home, you supply AC to the converter, which converts the AC to DC and charges the battery.
On the flip side, DC does not need a converter. When you do DC fast charging, the charger bypasses the converter and directly charges the battery. The vehicle’s Battery Management System controls the voltage, current, and temperature of the DC.
Since DC charging does not need a converter like AC charging, it is usually faster than AC charging. A DC quick charging station can not be installed at home, as our domestic connection can not handle the extreme voltage of DC.
DC charging requires expensive equipment and a high-voltage connection to the grid. It is therefore ideal for commercial purposes only, where you need to pay to get your vehicle fast-charged.
Depending on the power rating of the charging station, DC charging can usually charge your battery within an hour or two.
Since DC charging works in a high-voltage range, you might wonder if it is bad for batteries. But it is not.
Regular DC charging is not bad, although the battery degradation will be slightly more than with AC charging. Usually, it would be around 5% more than AC charging.
Conclusion: AC Charging Vs DC Charging
AC charging takes 6-7 hours to charge a 3-4 kWh battery with a 500W charger to 80%, whereas DC charging takes about an hour. That’s a huge difference.
It is advisable to use DC charging whenever possible because that will save charging time. However, remember that you need to spend more money on DC charging, and your battery will degrade faster than with AC charging.
If you are happy with overnight slow charging, then charging at home with an AC charger is the best option from both cost and battery life.
FAQ: AC Charging Vs DC Charging
What Is The Difference Between AC And DC Chargers?
The main difference between AC and DC chargers is that an AC charger uses a converter to convert AC to DC, whereas a DC charger does not need a converter.
Why Is DC Charging Faster Than AC?
DC does not need a converter to convert AC to DC, as the conversion is done at the charging station itself. Reducing this additional conversion step makes DC charging way faster than AC charging.