The solenoid valves are widely used in many processes across industries to control machines. The solenoid valve is a valve that is used to control the flow of fluid autonomously in various environmental conditions and applications to carry out its function efficiently.
What Is Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is a control unit that electrically controls the mechanical actions of the valve automatically without the need for manual operation by the action of the solenoid.
In general, the solenoid valve controls the opening or closing of the valve by controlling the orifice.

Solenoid Valve Working Principle
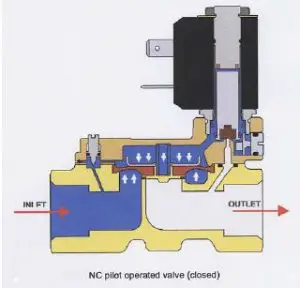
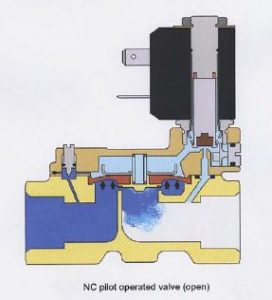
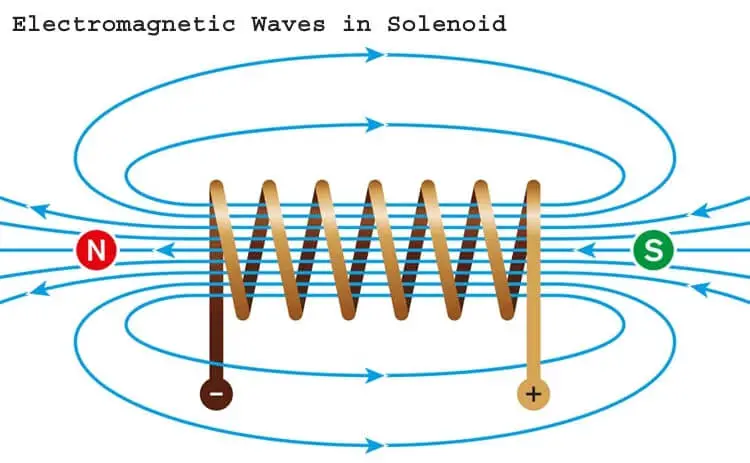
The solenoid valve is an electro-mechanical device that works based on the principle of electromagnetic mechanism. The electric current is passed through the coil of wire which will produce an electromagnetic field in the solenoid. At rest conditions, it can be either normally open or normally closed.
By energizing the solenoid, it produces the force to pull the plunger that opens the orifice which will allow the flow of the fluid.
When the solenoid is de-energized, the spring will push the solenoid to its initial position which will close the orifice of the valve and cuts the flow of the fluid.
Construction of Solenoid Valve
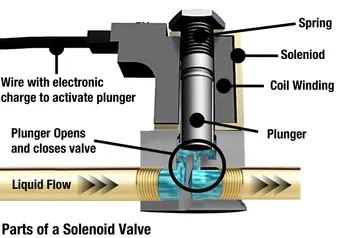
The solenoid valve mainly consists of 3 parts. They are solenoid, plunger, and valve body.
In a solenoid valve, a plunger which is a ferromagnetic core is surrounded by the coil of wire. The coil of wire is known as a solenoid that is used as an electromagnet. The valve body is the outer casing of the valve.
The valve body consists of an inlet and outlet port. Ports are responsible for the entry and exit of the fluid. The spring is located next to the plunger.
Materials selection of Solenoid valve
The material of the solenoid valve must be chosen carefully according to the properties and requirements to optimize its reliability and to make it cost-effective.
Valve body material
In the solenoid valve, the valve body is chosen based on the property of the fluid.
- For high temperature fluids – Polyphenyl Sulphide (PPS) and corrosion resistant steel is preferred. PPS have high melting point and it can be continuously used around 200 degree celsius. These materials will have high corrosion resistant property so it can be used for acids and alkalines.
- For neutral fluids – Brass and bronze are used to make valve bodies for neutral fluids like water.
- For low temperature fluids – Polyvinylidene Flouride has resistant to acid, base or alkaline and solvents but it cannot bear high temperature. It is suitable only for low or normal temperature fluids.
- For chemical fluids – Polyether Ether Ketone is an expensive material which provide high chemical resistant and promote effective sealing.

Solenoid material
The solenoid coil is made up of copper wire. Copper is used because copper is a good conductor of electricity and it consumes less voltage to produce the magnetic field.
The plunger or solenoid core is made up of ferromagnetic materials. The most commonly used ferromagnetic materials are ferronickel, electrical pure iron, alloy iron, Ferro aluminum, and Ferro cobalt.
Types Of Solenoid Valve
The solenoid valves are three types depends on the position of the plunger.
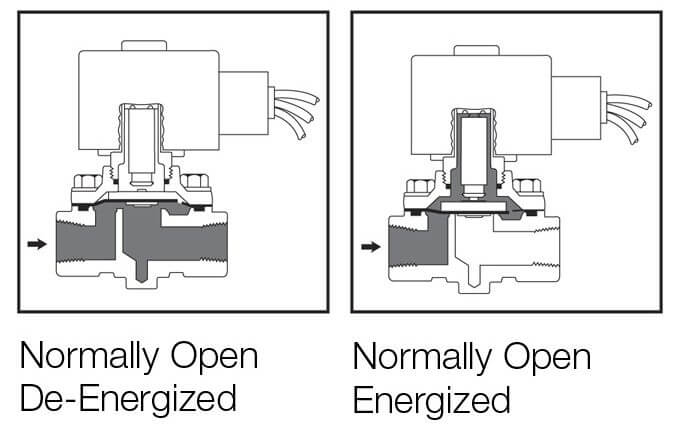
Normally open Solenoid valve
In a normally open solenoid valve, the plunger is down position and the valve is closed when the solenoid is energized. When the solenoid is de-energized, the valve will be in the open position and it will allow the flow of fluid. It is preferred when the solenoid valve is required to open for a long time.
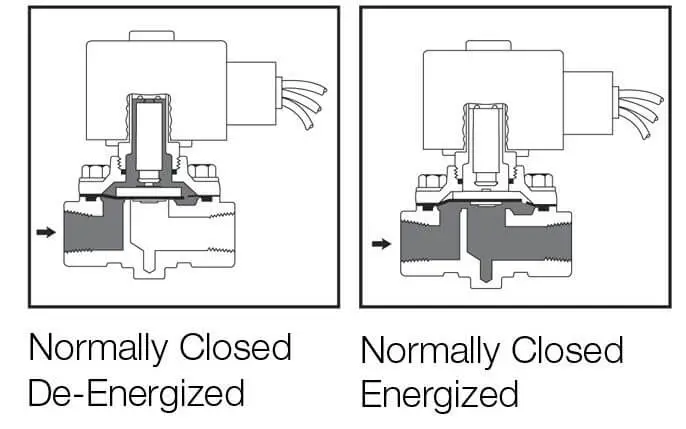
Normally closed Solenoid valve
In a Normally opened solenoid valve, initially, when the solenoid is not energized, the plunger is down and it is in the closed position. When the solenoid is energized, the plunger moves upwards and the valve will be opened. Here the fluid flow will take place when the solenoid is energized. When solenoid needs to be in the closed position for a long time.
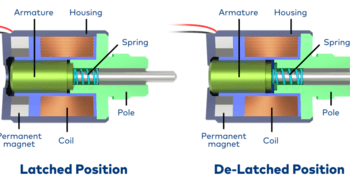
Bi-stable Solenoid valve
A bi-stable solenoid is also known as a latching solenoid. It is neither normally open nor normally closed type. It will have a semi-permanent magnet inside the solenoid core. A short electric pulse of direct current will activate the semi-permanent magnet and it will open the valve. By changing the polarity of the electric signal will remove the magnetic charge and it will close the solenoid valve. It remains to be in the same position (either open or close) until the application of the electric pulse.
Types Of Solenoid Valve based on operation
Based on the operation of the solenoid valve and its working principle, it has five main types. They are discussed below.
Direct acting Solenoid valve
A direct-acting solenoid valve operates directly without any external pressure. It lifts the valve directly by the electromagnetic mechanism. It is used for simple applications with a relatively less rate of flow. There is no minimum pressure to operate this valve but the maximum pressure and flow rate of the valve is depends upon the orifice.
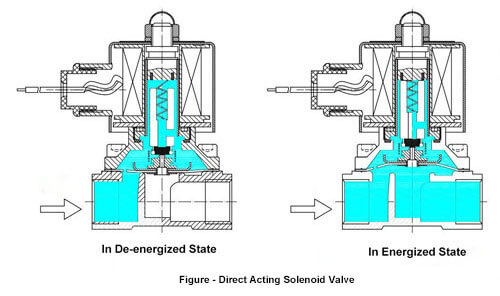
Pilot operated Solenoid Valve
Pilot operated valve cannot act directly. It is also known as an indirect-acting solenoid valve. It acts by the external pressure difference. 0.5 bar pressure is minimum to actuate the valve. It is preferred for high flow rate applications. It can be used for both normally open and normally closed valves.
At high pressure, the small piolet valve is used to open the large valve. It requires less energy to actuate it but the solenoid needs a power supply throughout the process to remain in an open state.
Two-way Solenoid valve
Two-way indicates two ports. they are
- Cavity port
- Body orifice port
Both the ports can be used alternatively to allow the flow of fluid or to cut off the flow of fluid. It is applicable for both normally open and normally closed valves.
Three-way Solenoid Valve
Three-way valve indicates 3 ports. It is preferred for the operation which requires exhaustive or alternate pressure. These 3 ports in the solenoid valve can be used in three different combinations. If one port is blocked by a plunger, then the other two ports are used for the inlet and outlet. It can be implied for various combinations of operations in industries.
- Mixing – Two inlets and one outlet.
- Diverting – one inlet and two outlets.
- Universal – It can work as an inlet or outlet (i.e) it will allow fluid in either direction but only two ports can be connected at a time.
Four-way Solenoid Valve
The four-way valve consists of four ports. It is used as a dual-acting actuator.
- 1st port – air supply
- 2nd port – Exhaust
- 3rd & 4th port – Cylinder ports
Selection of Solenoid Valve
While selecting the solenoid valve certain factors need to be considered.
- Medium – The type of fluid or media directly affects the valve and seal materials. So the valve materials must be chosen depends on the fluid used for the particular application.
- Environment – The different types of environmental conditions are outdoor environment, indoor environment, moist environment and explosive environment. The materials should be chosen after considering the environmental condition.
- Cost – Choose the material as per the required quality. Selection of valve type, material and supplier can have direct impact on cost.
- Safety – Food products need to consider the safety of the consumer. So the valves used for the production food must use the material which will not cause any harm to the consumer. Mostly stainless steels are used for this application.
- Valve specifications – The solenoidal valve specification should be decided after considering the pressure range, temperature range, IP rating, response time, voltage, valve type and valve size.
Solenoid Valve Applications
Solenoid valves are used almost in every field like medical instruments, manufacturing industries, agricultural equipment, beverage industries, automotive parts, locking systems, aerospace industries, etc, Let’s discuss a few of them below.
Compressor: Compressors have solenoidal valves for different purposes based on requirements. Mainly it is used to control the flow of air in the compressor by energizing and de-energizing the solenoid.
Water purifier: The solenoid valve is used in Reverse Osmosis (RO) water purifiers. It uses a flow sensor to detect the water level in a purifier. If the water reached its low level then the sensor detects it and it actuates the solenoid valve which will open the orifice and allow the water to be filled inside the purifier and the same process is carried out to cut off the water flow when it reached the upper level.
Beverage Industries: In the beverage industry, solenoid valves are used to fill up the bottles with appropriate levels and for the mixing of fluids at exact ratios.
Irrigation devices: In agriculture, solenoidal valves are employed in automatic sprinkler devices to irrigate the field by detecting the flow of water.
Conclusion
I hope you got a brief idea about solenoid valves, types, selection of solenoid materials, and their applications. If you have any doubts or questions, kindly leave them in the comments section.
You may also like to read: Types Of CNC machine
Are you looking for a job? Visit Jobsora which is one of the most innovative job search systems in the world
About The Author

Deepthi is a Production Engineering graduate from Government College of Technology, Tamilnadu. Mentoring students for 2+ years on technical and interpersonal skills. Co-founder of Edtech startup ‘KnackEdu’. Technical event organizer for 3+ years. Worked on various startups, automotive events, and research projects. Exploring the field of supply chain management, CAD, CAM, and FEA.