What is the one thought that comes to our mind when we hear the word ” Engine”. POWER. Yes, that’s the sole purpose of an engine. But do you know that there are different types of engines? Well, many of you might be aware of those types of engines. But this article is for those who are not aware of this.
The engine produces power. Power can be used to move the vehicle, aid in lighting or running accessories like an air conditioner, or even generate electricity, like in the case of a generator.
The use of engine power is not limited to what I mentioned above. If I start writing about the use of engine power completely, then it would be a huge book. Let’s not get into that and, for the time being, explore different types of engines in this article.
Different types of engine
How an engine produce power? By burning fuel. Right? If you broadly categorize types of engines, then there are two types of engines based on how fuel is burned. All other types of engines are the subtype of the below two categories.
- Internal Combustion Engine (IC Engine)
- External Combustion Engine ( EC Engine)
Internal Combustion Engine
In the internal Combustion Engine, the air-fuel mixture is burned inside a closed chamber. Due to the internal Combustion, high temperature and high-pressure gas create forces on internal components like a piston, rotor, blades that ultimately convert this force to work.
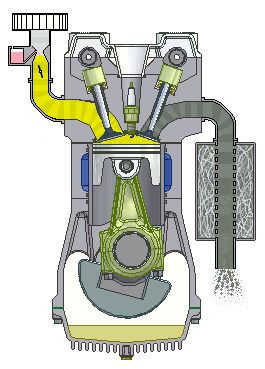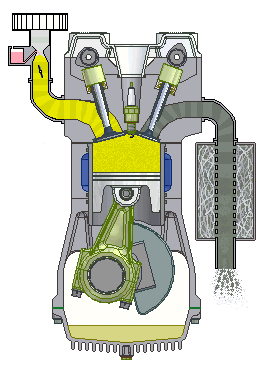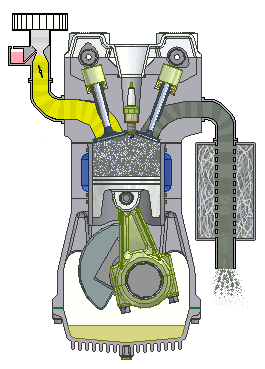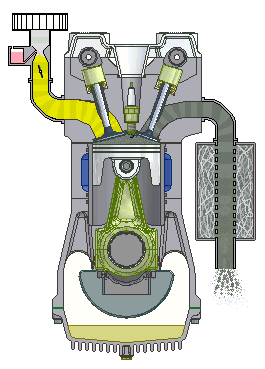
Example: Car, bus , motorcycle engines
External combustion engine
In the external combustion engine, the fuel air mixture is burned outside of the engine chamber .
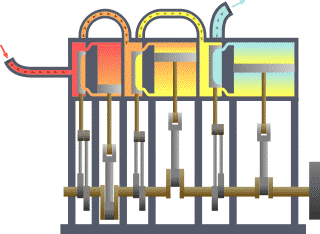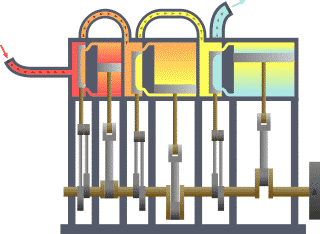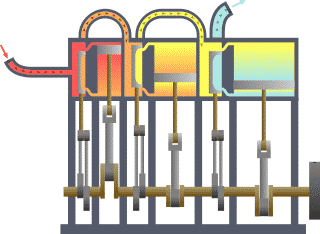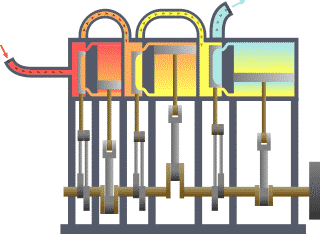
Example: Steam engine
Internal Combustion Engines are further classified into the following categories and each category has different types of engines.
- Type of design
- Number of cylinders
- Number of strokes
- Types of fuel used
- Cycle of operation
- Type of ignition
- Valve arrangement
- Cylinder arrangement
- Type of cooling
- Type of fuel injection
Type of design
Based on types of design, internal combustion engines are divided into two types.
- Reciprocating engines
- Rotary Engines
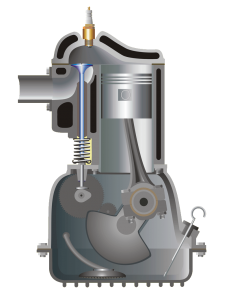
Reciprocating Engine
In a reciprocating engine, the piston moves to and fro ( reciprocating) inside the cylinder. That is why it is called reciprocating engines.
Rotary Engine
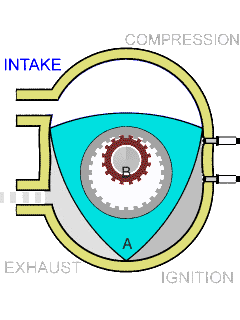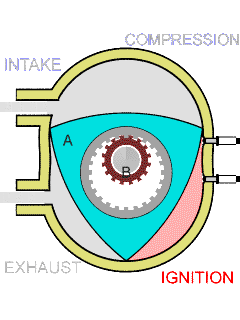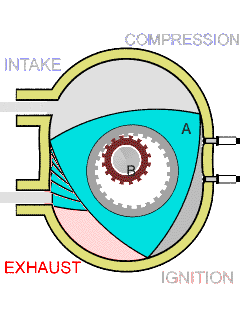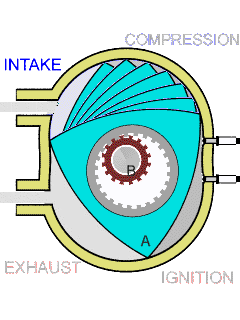
In the case of rotary engine, a rotor is used to produce power, there is only rotary motion and no reciprocating action.
Number Of Cylinders
Based on number of cylinders, IC engines are classified into below types
- Single cylinder
- Double cylinder
- Multi-cylinder
Single Cylinder Engine
In single cylinder engines, there is only one cylinder in the engine. Typical examples are motor cycle engines.

Double Cylinder Engine
In double cylinder engines, there is two cylinder in the engine. Examples are high end motorbikes, three wheelers.

Multi Cylinder Engine
In a multi-cylinder engine, multiple cylinders are used. Multi-cylinder is used in car engines, bus engines, or other engines used in automobiles.

Number of strokes
Based on number of strokes, engines are divided into two types.
- Two strokes engine
- Four strokes engines
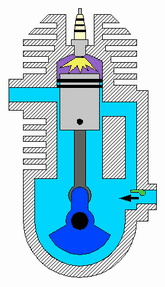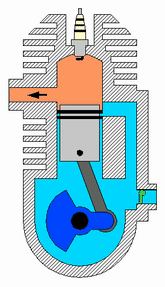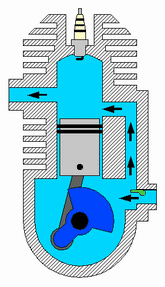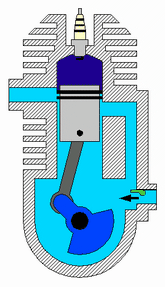
Two stroke engine
In two strokes engine, the piston moves upward ( from BDC to TDC) and downward ( from TDC to BDC) in the cylinder. So in total, there are two strokes. Typical examples are motorcycle engines.
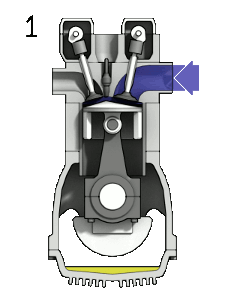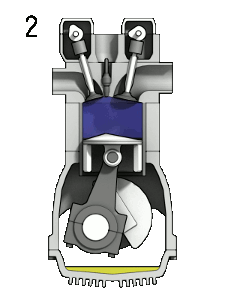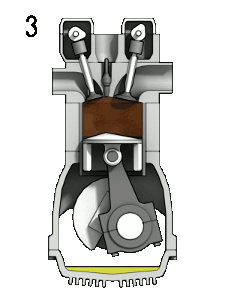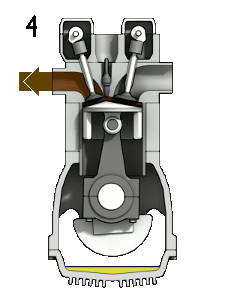
Four Stroke engine
The piston moves two times upward ( from BDC to TDC) and two times downward ( from TDC to BDC). So in total, there are four strokes. Typical examples are Car engines.
Types of fuel used
Based on types of fuel used, engines are divided into following types.
- Petrol engine
- Diesel engine
- Gas engine
- Multi-fuel engine
Petrol Engine
In the petrol engine, petrol is the fuel used for burning and generating force. That is why it is called a petrol engine. Normally almost all motorcycle engines are petrol engines.
Diesel Engine
When diesel is used as a fuel for burning then it is called a diesel engine. Normally all trucks and buses use diesel engine.
Gas Engine
This type of engine uses gas ( LPG, CNG, etc) as fuel to burn and produce power. Cars, buses, trucks can have gas engines.
Multi fuel engine
A petrol engine can be converted to work with both petrol and gas. If the engine can use both petrol and gas, then it is called a multi-fuel engine. Nowadays, many cars and buses use a multi-fuel engine.
Cycle of operation
Based on cycle of operations, engines are divided into following types.
- Otto Cycle
- Diesel Cycle
- Dual cycle
Otto Cycle
In the otto cycle , the energy produced after burning of fuel is released at constant volume.
Diesel cycle
In the diesel cycle, the energy produced after burning of fuel is released at constant pressure
Dual cycle cngine
In the dual cycle engine, the energy produced after burning of fuel is released at partly constant volume and partly at constant pressure.
Type of ignition
Based on the type of ignition, IC engines are divided into two types as shown below.
- Spark ignition engine
- Compression ignition engine
Spark ignition engine
As the name suggests, there is a spark plug that ignites spark after the air-fuel mixture is compressed for combustion in the spark-ignition engine. All petrol engines are spark-ignition engines.
Compression ignition engine
In the compression-ignition engine, there is no spark plug. The air-fuel mixture starts burning due to the excessive heat generated by the compression of the air-fuel mixture. All diesel engines are compression ignition engines.
You may like to read: What is octane number and cetane number
Valve arrangement
Based on valve arrangement IC engines are divided into following types
- L head engine
- T head engine
- I head engine
- F head engine
L Head Engine
In the L head engine case, valves are placed in the engine block beside the piston. It has a single crankshaft. In the L head engine, airflow needs to take a 90-degree turn to enter the cylinder. This type of engine has serious efficiency issues and can not be used in modern cars.

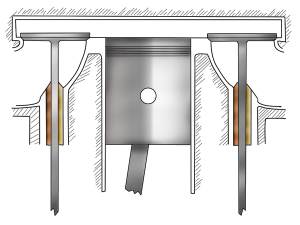
T Head Engine
In the T head engine, the inlet valve on one side, and the exhaust valve is on the other side, forming the shape of T. That is why it is called the T Head engine. It needs two crankshafts to operate.
I Head Engine
In I head engines, both entry and exhaust ports are placed on the cylinder head. These types of engines are widely used in automobiles.
F Head Engine
F head engines are basically a combination of L head, and I head engines. Inlet valves and ports are on the cylinder head like in the I head engine and operated by a pushrod. But the exhaust valve and part are placed beside the cylinder and parallel to the piston forming the shape of L. Exhaust ports are operated by a lifter in this case.
Cylinder Arrangement
Following are the types of engine based on the cylinder arrangements
- Horizontal Engine
- Vertical Engine
- V type engine
- W type engine
- Radial engine
- Opposed cylinder engine
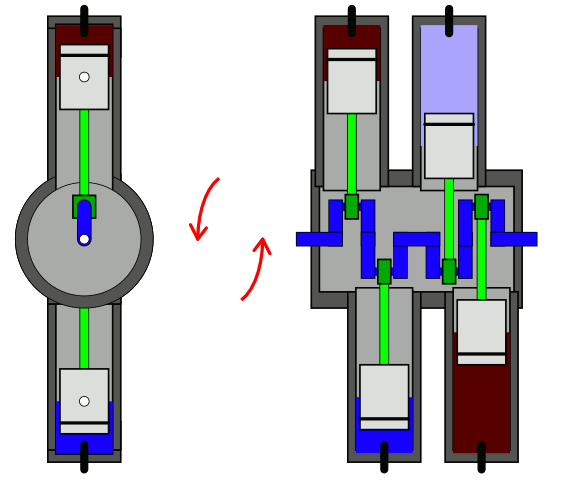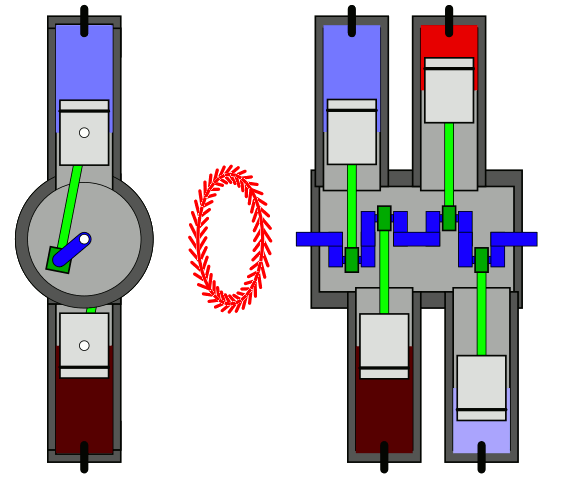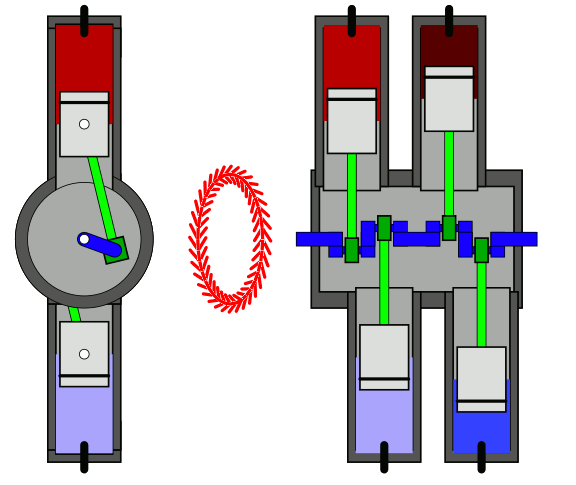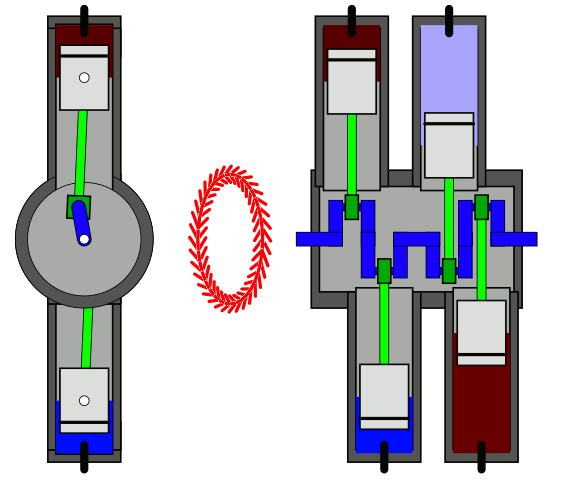
Horizontal Engine
In the horizontal engine, cylinders are placed horizontally.
Vertical Engine
In the vertical engine, cylinders are placed vertically inline with each other. This type of engine is very common in automobiles.

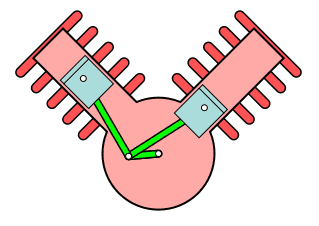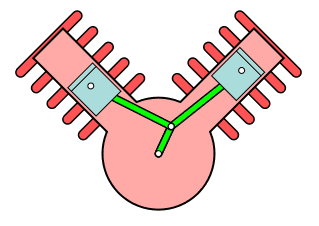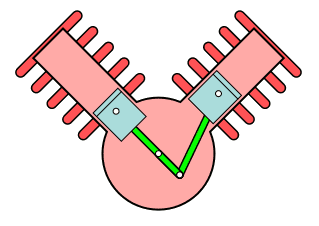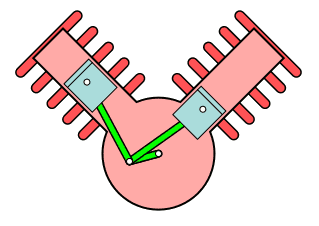
V type engine
This type of engine has a cylinder placed at an angle that usually looks like a V. This is the typical configuration of a two-cylinder engineer seen in high-end motorbikes.
W Type engine
In the W-type engines, cylinders are placed at an angle, and it looks like a W shape configuration. This is a typical configuration of the three-cylinder engine, but most automobiles use a three-cylinder engine in a vertical configuration.
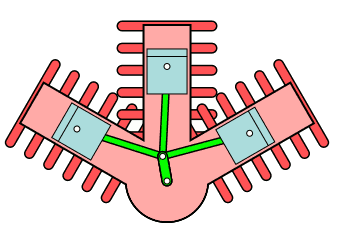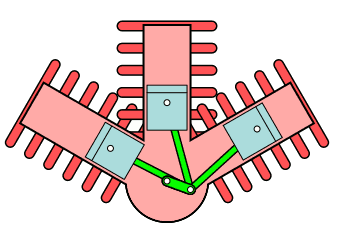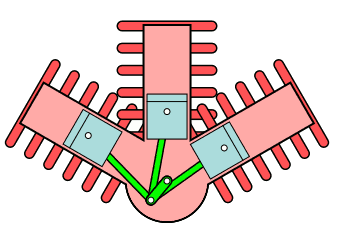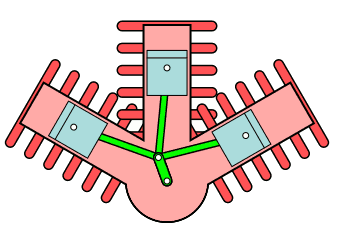
Radial Engine
In this type of engine, cylinders are placed in a radial configuration with a central crankcase. It looks like spokes of wheels.
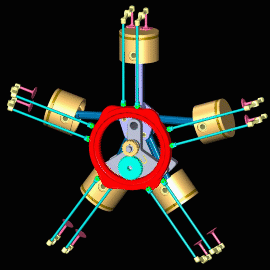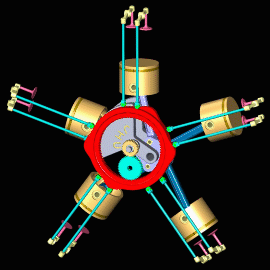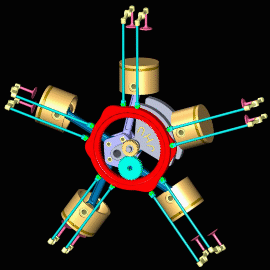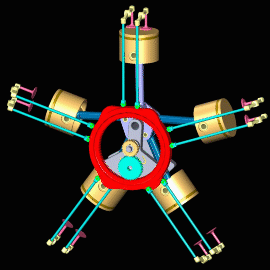
Opposed Cylinder Engine
In the opposed cylinder engine, cylinders are placed opposite to each other. So although the engine size becomes large due to this type of configuration, it offers more load balancing.
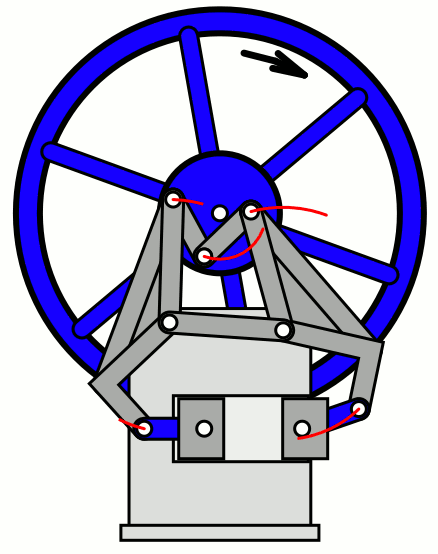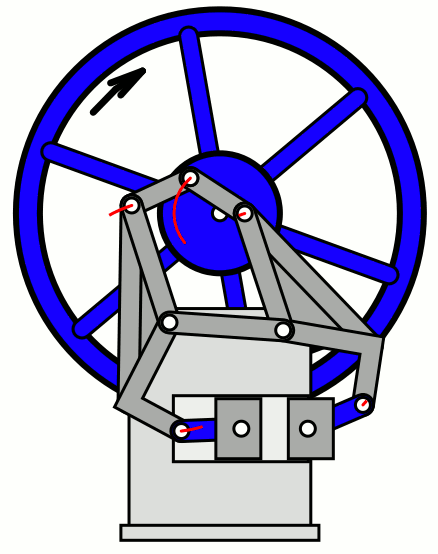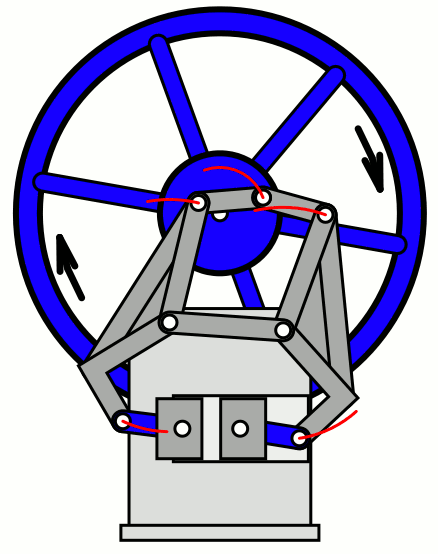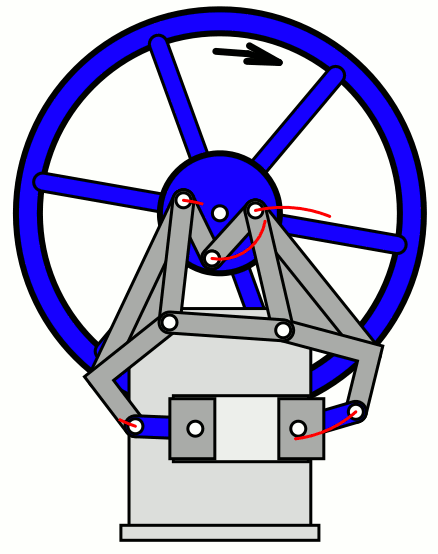
Types of Cooling
Engines are divided into following categories based on types of cooling
- Air Cooled engine
- Water-cooled engine
- Oil cooled engine
Air cooled engine
In an air-cooled engine, the engine gets cooled by natural air. The cylinder has many fins that increase the surface area for better cooling. This type of cooling is generally used in motorcycles and scooters, where the natural flow of air is readily available.
Water cooled engine
In a water-cooled engine, water is used to cool the engine. Generally, anti-freezing solutions are added to the water so that in the cold season, water does not become ice. These types of engine radiators flow the coolant that aid in engine cooling. Most of the cars, trucks, or buses use this type of cooling.
Oil cooled engine
Oil cooled engine oil as a cooling medium. This type of engine is popular in high end motor bikes and cars.
Types Of fuel Injection
Engines are classified into following types based on types of fuel injection.
- Carburetor engine
- Air Injection engine
- Solid injection engine
Carburetor Engine
A carburetor engine uses a carburetor that mixes the air and fuel correctly before it is injected. This is common in petrol engines.
Air Injection Engine
In the air, injection engines are typical diesel engines. This type of engine does not use a carburetor, and the air-fuel mixture is directly fed through a feed pump.
Solid Injection Engine
Solid injection engines are often called airless injection engines, where the fuel is directly fed into the combustion chamber without air.
Conclusion
That’s all we have in this article. In this article, I tried to give a glimpse of different types of engines. I understand there are other types of engines based on different categories. But those are special case scenarios. Whatever is mentioned in this article is the one primarily used in the industry.
If you have any questions or queries, please do write in the comment section and I will be happy to help.



