An evaporator is a device to convert liquid from a liquid state to a gas state. For example, in a refrigerator, the evaporator is used to take the heat out of the refrigerator cabinet and dissipate it into the atmosphere through a condenser.
In this article, we will talk about different types of evaporators, their uses, and their applications of evaporators.
What Is Evaporator?
An evaporator is a device that does evaporation. Evaporation means converting liquid to a gas state. An evaporator is used in applications where heating, ventilation, and cooling need to be done
Types of Evaporator
- Batch Evaporator
- Short-Tube Vertical Evaporator
- Horizontal Tube Evaporator
- Falling Film Evaporator
- Rising/Falling Film Evaporator
- Long-Tube Vertical Evaporator
1. Batch Evaporator
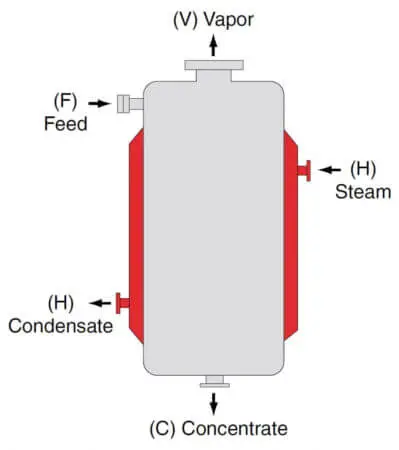
Batch pan evaporators are the oldest type of industrial evaporators. Batch pans use a spherical vessel that is heated by a steam jacket or heating element. The water in the product evaporates and is collected in a separate condenser. Large batch pan evaporators have capacities of 5,000 – 10,000 gallons.
Advantages Of Batch Evaporator
- Effectively separate the vapor from the liquid concentrate
- Meet the conditions required by the product being processed
- Produce a product that meets the required quality
- Be energy-efficient, where possible making effective use of steam with multiple-effect evaporation or vapor recompression
Disadvantages Batch Evaporator
- high head-room requirements
- higher pressure drop through the tubes than in a falling film evaporator
- hydrostatic head at the bottom of the tubes may increase product temperature and cause temperature-sensitivity problems
2. Short-Tube Vertical Evaporator
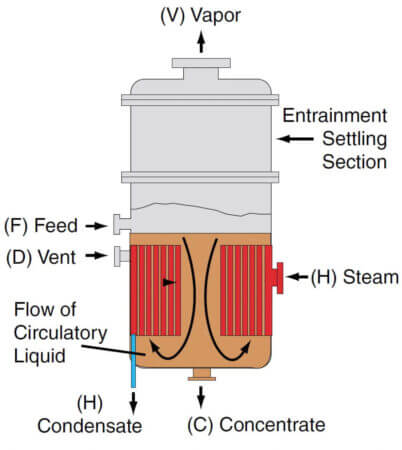
Short-tube vertical evaporators are the oldest but still widely used in the sugar industry in the evaporation of cane-sugar juice. These are also known as calandria evaporators. It became so common in the process industry that this evaporator is sometimes known as
a standard evaporator. Short-tube vertical evaporators consist of a short tube bundle enclosed in a cylindrical shell. This is called calandria.
The feed is introduced above the upper tube sheet and steam is introduced to the shell or steam chest of the calandria. The solution is heated and partly vaporized in the tubes.
The central tube in a calandria is of longer diameter. Typically its downcomer area is taken as 40 to 70% of the total cross-sectional area of tubes. The circulation rate through the downcomer/downtime is many times the feed rate. The flow area of the downtake is normally approximately equal to the total tubular flow area.
Advantages Of Short Tube Vertical Evaporator
- Low head space required.
- Suitable for liquids that have a moderate tendency to scale, since the product is on the tube side, which is accessible for cleaning.
- Fairly high heat-transfer coefficients can be obtained with thin liquids.
Disadvantage Of Short Tube Vertical Evaporator
- high head-room requirements.
- higher pressure drop through the tubes than in a falling film evaporator.
- hydrostatic head at the bottom of the tubes may increase product temperature and cause temperature-sensitivity problems.
3. Horizontal Tube Evaporator
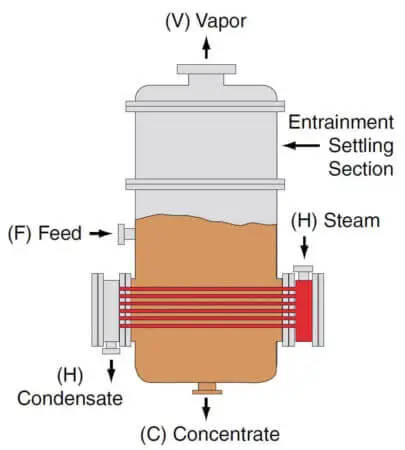
The principle mechanism involved in this type of evaporator is that steam is passed through tubes arranged horizontally. Heating causes evaporation of the feed outside the tubes discharging concentrate at the bottom and vapors passed out from the outlet at the top
It consists of a vertical cylindrical body with a dome-shaped top and bottom part made of cast iron. The lower part of the cylindrical body is fitted to a steam inlet and outlet for condensate.
Inside the cylinder horizontal tubes are placed. Horizontal tubes are 6 to 8 in number and made of stainless steel. The lower portion also consists of a vent for noncondensed gases. Feed inlet is also provided. There is one outlet for vapor at the top of the vessel, and the concentrated product is discharged from the bottom of the body.
Advantages of Horizontal Tube Evaporator
- Relatively low cost for small-capacity applications
- Low headroom requirements
- large vapor-liquid disengaging area
- Relatively good heat transfer with proper design
- The potential for easy semiautomatic descaling
Disadvantages Of Horizontal Tube Evaporator
- Not suitable for viscous liquid
- They have a smaller capacity than other evaporators.
4. Falling Film Evaporator
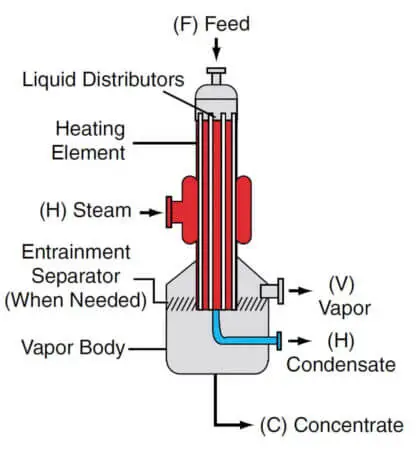
The falling film evaporator is largely used for the concentration of fruit juices and heat-sensitive materials because of the low holdup time. The device is suitable for scale-forming solutions as boiling occurs on the surface of the film.
In a falling film evaporator, the liquid is fed at the top of the tubes in a vertical tube bundle. The liquid is allowed to flow down through the inner wall of the tubes as a film.
As the liquid travels down the tubes the solvent vaporizes and the concentration gradually increases. Vapor and liquid are usually separated at the bottom of the tubes and the thick liquor is taken out.
Evaporator liquid is recirculated through the tubes by a pump below the vapor-liquid separator. This type of evaporator is illustrated in. The distribution of liquid in the inner wall of the tubes greatly affects the performance of this type of evaporator.
Advantages Of Falling Film Evaporator
- Relatively low cost
- Low product hold up
- Small space requirement
- Good heat transfer
Disadvantages Of Falling Film Evaporator
- It requires high headroom
- Not good for salting and scaling materials
- Recirculation is required
5. Rising/Falling Film Evaporator
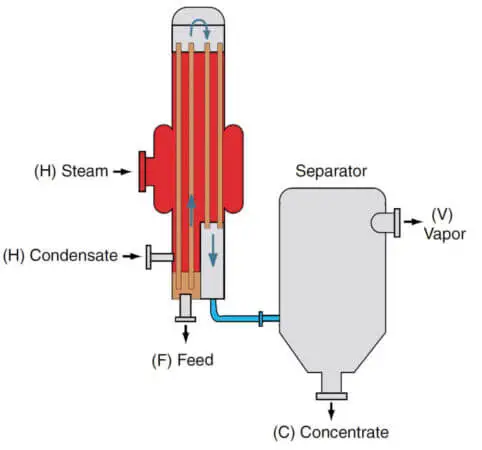
These evaporators combine the advantage of the ease of feed distribution of the rising film with the usual advantages of a falling-film unit. Vapor-liquid separation takes place at the bottom of the unit; the flow of liquid and vapor is always co-current. The LTV evaporator is frequently called a rising or climbing film evaporator.
The liquid starts boiling at the lower part of the tube and the liquid and vapor flow upward through the tube. If the heat transfer rate is significantly higher, the ascending flows generated due to the higher specific volume of the vapor-liquid mixture, cause liquid and vapor to flow upwards in parallel flow. The liquid flows as a thin film along the tube wall.
This co-current upward movement against gravity has the advantageous effect of creating a high degree of turbulence in the liquid. This is useful during the evaporation of highly viscous and fouling solutions.
Advantages Of Rising/Falling Film Evaporator
- Relatively low residence times
- Relatively high heat transfer rates
- Relatively low cost
- Large units can be manufactured
- Low hold-up
- Small floor space requirements
- Good heat transfer over a wide range of services
Disadvantages Of Rising/Falling Film Evaporator
- High head-room requirements
- Recirculation is frequently required
- Generally unsuited for salting or severely fouling fluids
6. Long-Tube Vertical Evaporator
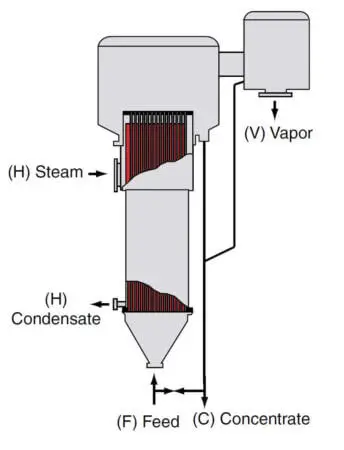
The long tube vertical and the rising-film evaporator is a widely used tabular evaporator. The long tube can be built as a large unit partially due to the high heat transfer performance under most conditions. Because of the simplicity and low cost of construction. It is basically a shell and tube heat exchanger mounted to a vapor separator.
Well, it required little floor space and high headroom. In the lower section of the tubes, the feed is heated up to the boiling point. At some point, bubbles form on the tubes, and boiling begins, increasing the rate of heat transfer. In this bubble zone, slugs of liquid and bubble rise too fast through the tube and discharge at high velocity from the top.
Advantages Of Long-Tube Vertical Evaporator
- Reduced floor space requirements.
- Relatively high heat-transfer coefficients due to partial two-phase flow.
- Ability to handle foamy liquids.
Disadvantages Of Long-Tube Vertical Evaporator
- High head-room requirements.
- Higher pressure drop through the tubes than in a falling film evaporator.
- The hydrostatic head at the bottom of the tubes may increase product temperature and cause temperature-sensitivity problems.
Conclusion: Evaporator Types
I hope you all got a fair idea about what is evaporators and the types of evaporators. if you have any questions on evaporator types, please write in the comment section and I will be happy to respond to you back.
You may also like to read: Different Types of Valves



