Laser Beam Machining is a non-conventional machining process in which the metal from the workpiece is removed by thermal energy. This process is widely used in industries, especially for brittle material with low conductivity. Let us learn more about laser beam machining in this article with the working principle and applications.
But before we learn more about laser beam machining, we need to learn about laser and types of laser.
What Is Laser?
The full form of laser is Light Amplification By Stimulated Emission Of Radiation. A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The key difference between a normal light source and a laser is coherence, directionality, monochromaticity, and high intensity.
Normal light has different wavelengths and intensities. That is why the photons emitted by an ordinary light source are spread across a large amount of surface, which is why it is incoherent.
In contrast to normal light, light waves of laser have the same wavelength and intensity. That is why light emitted by the laser is called monochromic light.
The light emitted from the laser can be very narrow and can focus on a very small area with high intensity. That is, more energy is concentrated on a small area causing the workpiece to heat up and melt the surface.
The laser is used in various machining operations, optical disk drives, photo printers, barcode scanners, car headlights, etc.
Types Of Laser
There are three types of laser based on the media that is used for the production of laser.
- Gas lasers
- Solid-state lasers
- Liquid lasers
Laser Beam Machining uses a solid state laser called Rubi Crystal for generation of laser beam.
What is Laser Beam Machining?
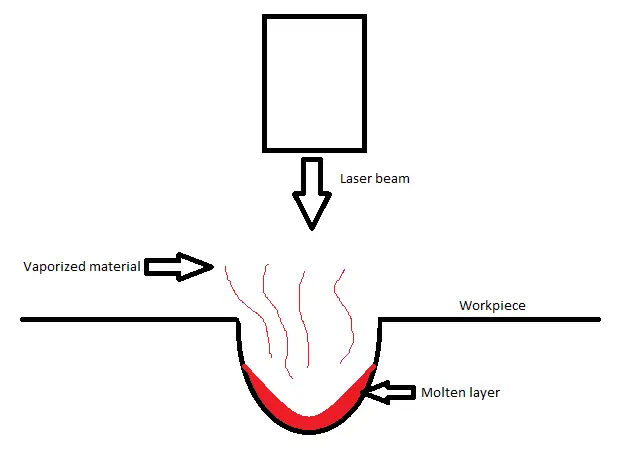
Laser beam machining is a machining process where high intense laser light is focused on a small area of a workpiece, causing that area to melt due to extreme heat and then vaporizes to remove material. Laser beam machining uses thermal energy to remove material from the workpiece.
Laser beam machining can be used in metallic and non-metallic workpieces. It is specially used for very high brittle materials where traditional machining can not be used. Also, when you need to create tiny shapes or cuts on a workpiece that traditional machining can not do, laser beam machining comes to the rescue.
Laser Beam Machining Working Principle
The laser beam emits monochromic light to focus on a very small area of the workpiece. Due to less surface area and high intensity of the laser, extreme heat was generated. That heat causes the metal to melt, and ultimately the molten metal gets vaporize. That is the basic working principle of a laser beam machining process. Now let’s learn the working principle in detail.
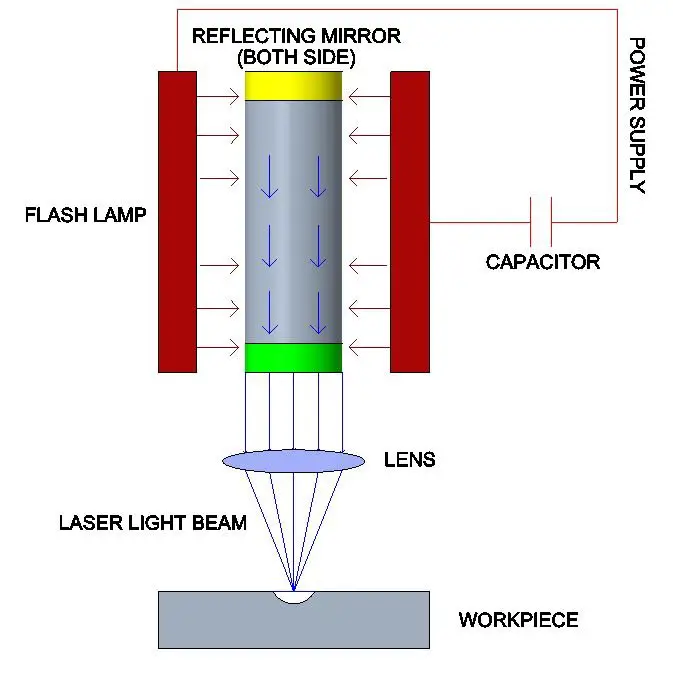
As you can see in the image that there is a cylindrical ruby crystal laser medium with two flat reflecting mediums is placed in a coil of flash lamps of about 1000W. The flash lamp emits high intense white light that excites the crystals to create a laser beam made to focus on the area of the workpiece using a lens.
The laser beam produced has a power density of about 1000 kW/cm2. Due to this extreme power density, heat is generated that melts the area of the workpiece.
Laser Beam Machine Key Components
Here are a few key components of a typical laser beam machine.
- Power Supply
- Flash Lamp
- Capacitor
- Laser Medium
- Reflecting Mirror
- Lens
Power Supply
As the name suggests, the power supply unit supplies power to the flash lamp so that it emits light to excite the electron from the lower level to a higher level in the laser medium.
Flash Lamp
Flash lamp is used to supply high intense white coherent light to the laser discharging tube/laser material that eventually excites the electron
Capacitor
A capacitor is used in the laser beam machining to operate the flash lamp in pulse mode as we know that the main job of a capacitor is to store charge and release when required.
Laser Medium / Laser Discharging Tube
In laser beam machining, Ruby crystals are used. When the flash tube emits light, it emits light photons containing energy, and the ruby crystal absorbs this light photon.
Reflecting Mirror
There are two types of reflecting mirrors used in laser beam machining. One is 100% reflective, and the other one is partially reflective. The laser beam emits through the partially reflective mirror.
Lens
A lens is used to focus the laser beam to the specified area of the workpiece.
Advantages Of Laser Beam Machining
- Very useful for machining brittle materials
- Can be used for metal and non-metals
- No contact between the tool and the workpiece
- No mechanical work involved
- No mechanical property is changed during the process
- Can create features in areas where other machining tools can not reach
- Capable of producing very precise features
Disadvantages Of Laser Beam Machining
- The Initial Set up cost is high
- A trained technician is required
- Low production rate
- Flash lamp life is short
- Very high energy is required
- The low material removal rate
- Very high maintenance cost
Application Of Laser Beam Machining
- Laser beam machining is used in almost every sector for producing precise and complex parts that are critical to the functionality of the product.
- It is used in medical science for hair removal and cosmetic surgery
- Very popular in a mass macro machining operation
- Used for machining small holes where traditional machine tools can not reach
- Complicated welding of non-conductive and refractory materials.
Conclusion
That’s all we have in this article. I hope you got a fair idea about laser beam machining. I understand that this article provides only the basics of laser beam machining. But still, if you have questions or queries, please write in the comment section, and I will be happy to respond.
You may also like to read: What is abrasive jet machining
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
What Is laser beam machining?
Laser beam machining is a non-conventional machining process where a laser beam is focused on a certain area of a workpiece to melt and vapourize to remove the material
What is LASER stands for?
Light Amplification By Simulating Emission Of Radiation



