Nanofiltration Vs Reverse Osmosis: Selecting the correct water filtration technology is essential to purifying water without wasting extra resources and money on unnecessary technologies.
Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration are two advanced water filtration technologies that are widely available. RO is an all-in-one solution for water filtration when the TDS level is very high.
Installing an RO where the water TDS level is already less than 300 wastes money, as Nanofiltration is enough to do the job for you.
In this article, let’s learn more about the difference between Nanofiltration Vs Reverse Osmosis.
What is Nanofiltration?
Nanofiltration is a membrane filtration process that falls between reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration.
It is designed to remove many molecules from the water, including divalent ions and large organic molecules.
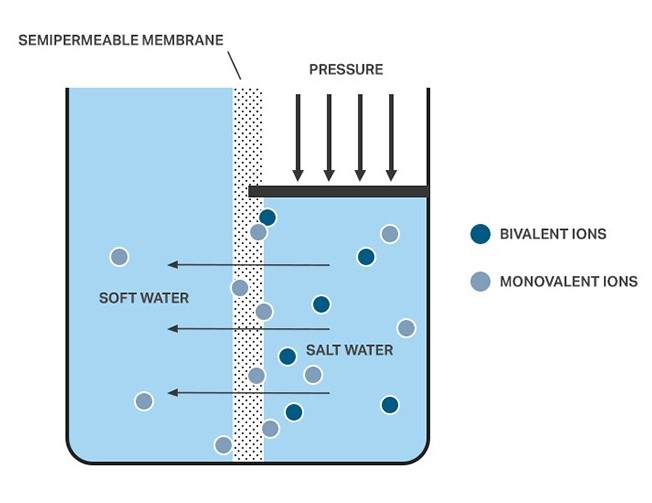
How Nanofiltration Works
Nanofiltration uses a semi-permeable membrane with tiny pores, typically ranging from 1 to 10 nanometers.
When water is forced through the membrane, the smaller particles and ions can pass through, while the larger molecules and ions are retained.
This process effectively removes unwanted substances from the water, leaving it clean and purified.
Applications Of Nanofiltration
Nanofiltration is commonly used for water softening, color removal, and the removal of specific ions such as nitrate, sulfate, and fluoride.
It is also used in the food and beverage industry to concentrate and fractionate components such as lactose and protein.
What Is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. It is a highly effective method for producing clean and pure water.
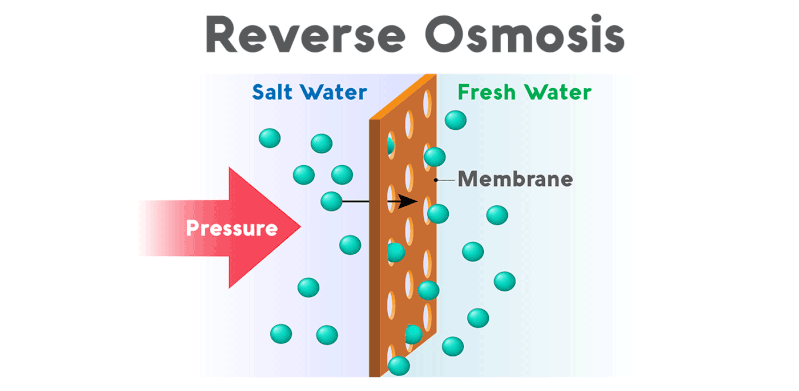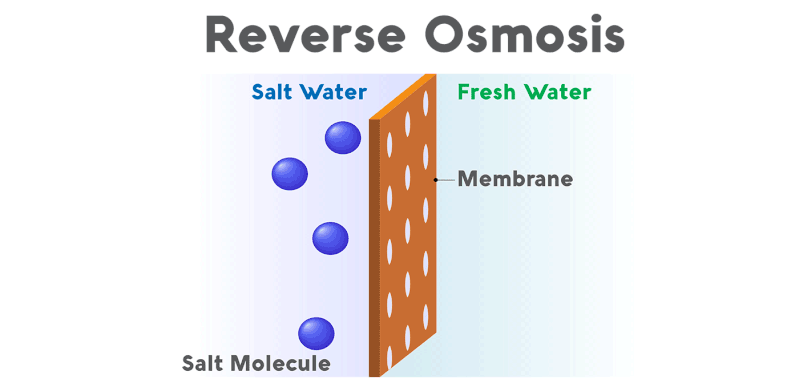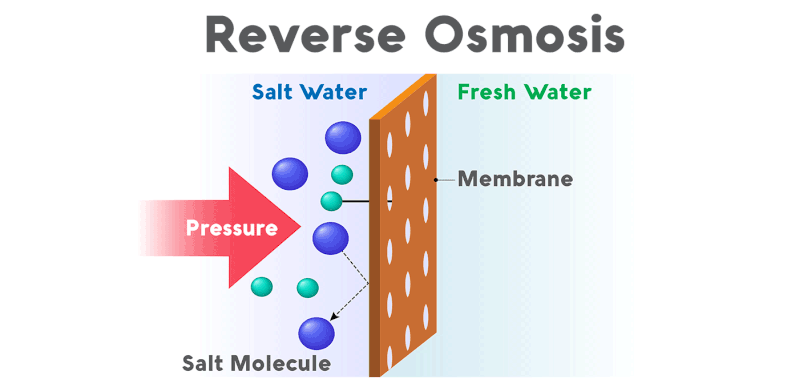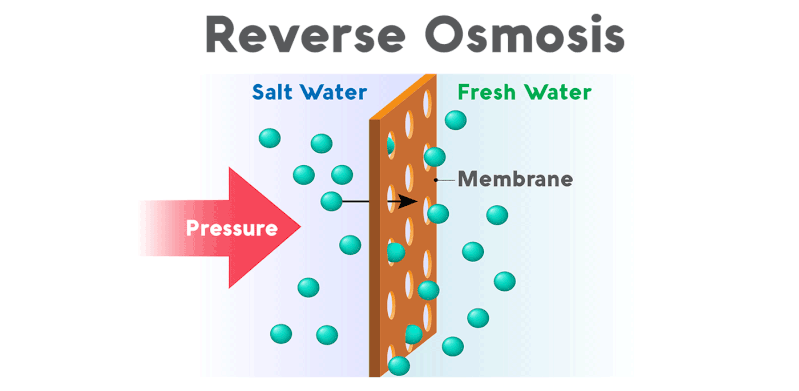
How Reverse Osmosis Works
Reverse osmosis applies pressure to the water, forcing it through a semi-permeable membrane. The membrane has tiny pores, typically around 0.0001 microns, which can effectively remove contaminants such as salts, bacteria, and other impurities from the water.
The result is clean, purified water suitable for drinking and other applications.
Applications Of Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is widely used for desalinating seawater, producing drinking water, and treating wastewater.
It is also used in the pharmaceutical and food industries to produce purified water for various processes.
Nanofiltration Vs Reverse Osmosis: What’s The Difference?
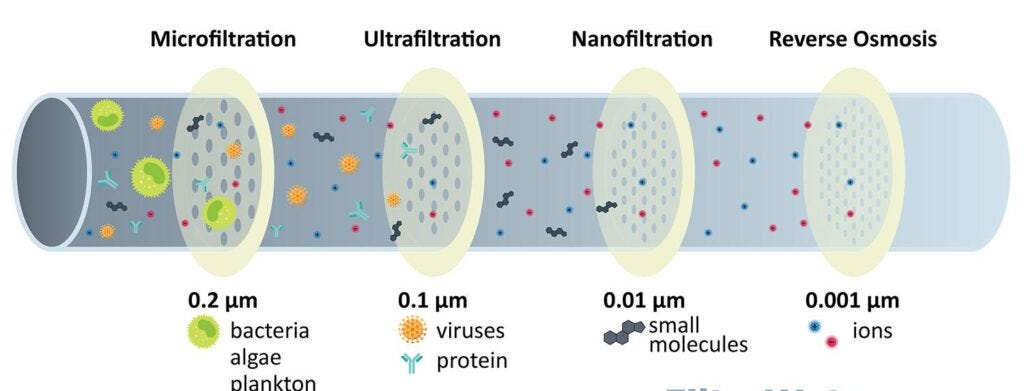
Pore Size And Filtration Level
The main difference between nanofiltration and reverse osmosis lies in the size of the pores in the membrane.
Nanofiltration membranes have larger pores than reverse osmosis membranes, allowing the passage of certain ions and molecules that would be rejected by reverse osmosis.
Energy Consumption
Nanofiltration generally requires less energy than reverse osmosis, as it operates at lower pressures and allows some ions and molecules to pass through the membrane.
Rejection Of Contaminants
Reverse osmosis is more effective at rejecting a wider range of contaminants, including salts, bacteria, and viruses, than nanofiltration.
This makes reverse osmosis the preferred method for producing highly purified water.
Water Pressure Requirements
Reverse osmosis typically requires higher water pressure to operate effectively, while nanofiltration, due to its larger membrane pores, can operate at lower pressures.
Pros And Cons of Nanofiltration
Advantages Of Nanofiltration
- Lower energy consumption
- Ability to selectively remove specific ions and molecules
- Lower operating pressure requirements
Disadvantages Of Nanofiltration
- Less effective at removing a wide range of contaminants compared to reverse osmosis
- Limited applications for producing highly purified water
Pros And Cons Of Reverse Osmosis
Advantages Of Reverse Osmosis
- Highly effective at removing a wide range of contaminants
- Suitable for producing highly purified water for drinking and industrial use
Disadvantages Of Reverse Osmosis
- Higher energy consumption
- Higher operating pressure requirements
- Removes beneficial minerals along with contaminants
Conclusion: Nanofiltration Vs Reverse Osmosis
In conclusion, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis are effective methods for purifying water, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The choice between the two depends on the application’s specific requirements, such as the level of purity needed and the energy and pressure constraints.