If you stretch a rubber band, you will notice that up to some extent it will stretch. Once you stop stretching, the rubber band will come to its original shape. That is called the elasticity of a material. Young’s Modulus is based on that principle. Let’s discuss more on Young’s Modulus in this article and figure out its definition, formula, and usage.
Before we learn about elasticity, we need to know below terms first.
What Is Stress?
The force per unit area is called Stress. When a body is subjected to a deforming force, a resultant restoring force occurs in the body which is equal to the deforming force but acts in the opposing direction. This restoring force per unit area is called stress.
For example, if the force applied is denoted by F and the unit area is A, The stress equation would be Stress = F/A. Every material comes under stress when it is subjected to an internal or external force.
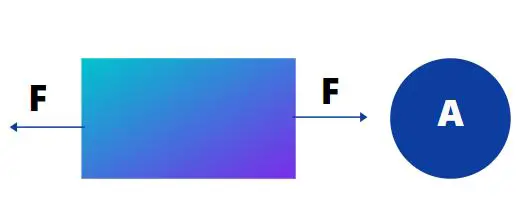
Stress= Force (F)/ Unit Area (A)
What Is Strain?
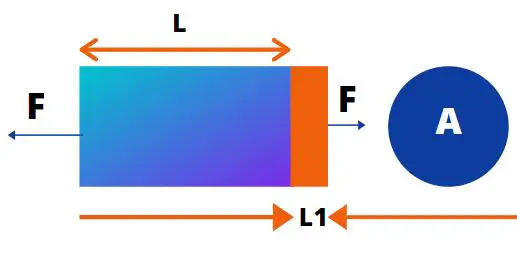
When a body is subjected to external force, it is either get elongated or contracted. The ratio of the amount of elongation to the original length is called Strain.
In the below example, the blue highlighted body is subjected to external force F. The initial length of the body is L. Due to the load the body is elongated by L1. So the strain, in this case, will be Strain= L1/L
Strain = Elongation/ Original length = L1/L
What is Young’s Modulus?
Young’s Modulus is the ability of any material to resist changes due to force acting in a longitudinal direction. Often Young’s modulus is called Modulus of Elasticity. Young’s Modulus is named after British scientist Thomas Young
Any rigid body will undergo deformation when any compression or tension load is applied. Up to some limit, stress is proportional to strain( Zone O-A). What that means is that if you apply more stress, more strain will occur. This is called Hooke’s law. The coefficient of proportionality is called Young’s Modulus. So higher the value of Young’s Modulus, more stress is required to create the same amount of strain.
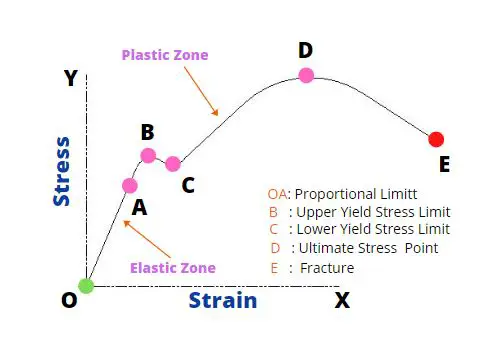
Young’s modulus holds good only when the stress is proportional to strain, which means under the elastic limit or elastic zone. This is there where the material comes back to its original shape if the load is withdrawn.
Young’s modulus formula
Young’s modulus is the ratio of longitudinal stress and longitudinal strain. Please keep in mind that Young’s modulus holds good only with respect to longitudinal strain.
If we look into the above examples of Stress and Strain then the Young’s Modulus will be Stress/Strain= (F/A)/(L1/L)
Young’s Modulus= Stress / Strain ={(F/A)/(L1/L)}
Young’s modulus unit
The unit of Young’s modulus in the English system is pascal per square inch ( PSI) and in the metric system, it is Newton per square meter (N/M2)
You may like to read: What is factor of safety?
Usage Of Young’s modulus
Young’s modulus helps engineers to find out at what stress the part is going to get into the plastic zone and eventually fails. That determines the load that a part can withstand.
In Construction projects, we use a lot of beams that are subject to extensive force. Young’s modulus is a key factor to decide the structural stability of those beams.
Young’s Modulus of Steel , Aluminium and other materials
| Materials | Young’s Modulus ( MPsi) |
|---|---|
| Steel | 30 |
| Aluminum | 10 |
| Polypropelene | .22-.29 |
| Polycarbonate | .29-.36 |
| PET | .29-.39 |
| Wood | 1.60 |
| Concreate | 4.35 |
| Glass | 7.25 |
| Bronze | 13.9-17.4 |
| Brass | 14.5-18.1 |
| Titanium | 16 |
| Cupper | 17 |
| Wrought Iron | 27.6-30.5 |
| Diamond | 152-175 |
| Tungsten | 58-59 |
| Nylon | .29-.58 |
| Polystyrene | .44-.51 |
| Silicon | 18.9-26.8 |
You may also like to read: What is CNC machine? Types of CNC machine
Benefits of Young’s modulus
- Helps to find out the linearity between stress and strain
- Predicts stress limit at which the parts get into plastic zone
- Provides information about when the part might fail
- Offers key insights about structural rigidity of materials
- Determine the deflection of a beam in different loading condition
Conclusion
Young’s modulus is a key parameter to qualify a material for an application subjected to different loading conditions. It provides key insights into the structural rigidity of materials.
I tried to cover the basics of Young’s modulus in this article which may help you consider during any product design project. I personally look into Young’s modulus whenever I have to choose a material for my project.
I hope you got a fair idea about Young’s modulus in this article. If you have questions or queries, please do write in the comment section and I will be happy to assist you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Stress?
Force per unit area is called Stress
What is the strain?
The ratio of the amount of elongation to the original length is called Strain
What is Young’s modulus?
The ratio of stress to strain is called Young’s modulus
What is Young’s modulus of steel?
30 MPSi
What is the Young’s modulus of aluminum?
10 MPSi