Dial indicators are small measuring tools that determine how far off a mechanical part is from its normal state. This article will teach dial indicators, their construction, types, working principles, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is a Dial Indicator?
A dial indicator is a compact device that precisely measures distances between two points or determines how far one place is from another. It has wide application in manufacturing facilities. It functions by illustrating the relative separation of many factors.
Dial indicators are also called Dial Gauge.

Construction of a Dial Indicator:
A dial indicator can be built differently depending on its type. For instance, engineers use two common dial indicator shapes, sector and circular. However, no tool or workpiece can be accurately measured with sector-type dial indicators.
Engineers rely on it frequently to get the most precise readings possible. In addition, the dial indicators of the sector type have a very small usable range.
Following are some major parts of a dial Indicator.
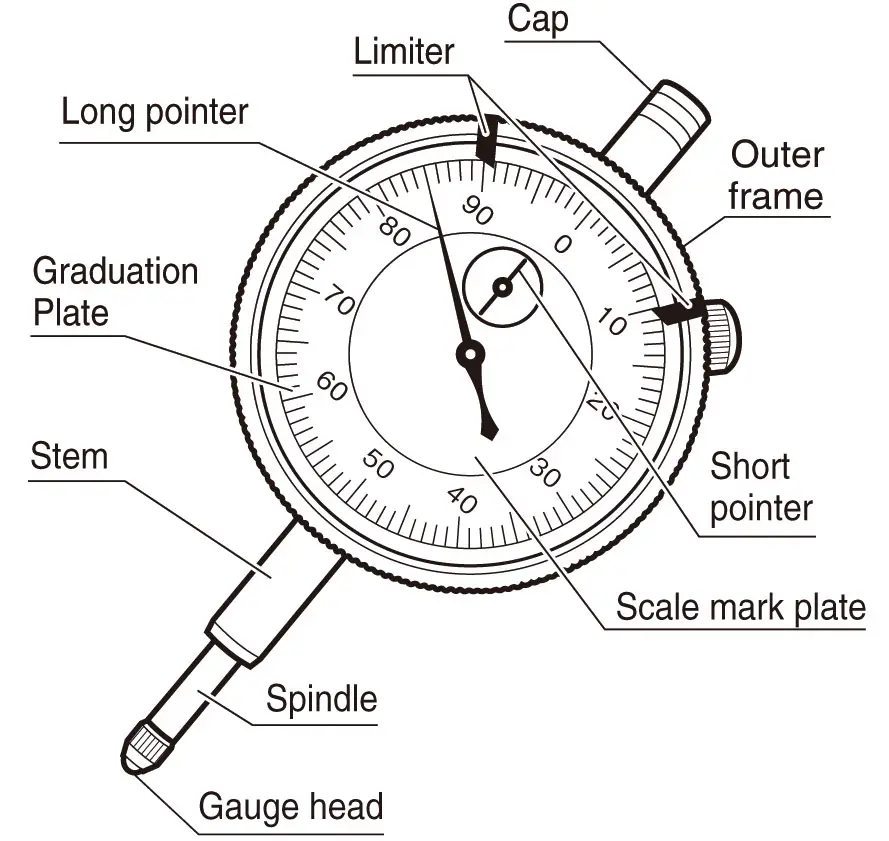
Graduated dial and needle
It is the most essential part of a dial indicator because it makes contact with the measured surface. Also, the needle and dial can keep track of every minute change in the machine part, which the indicator can then measure.
Embedded clock face and needle:
These are used to keep track of how many times the main dial’s needle has been rotated, and they are much smaller than the graduated dial and needle.
Plunger
This section is the dial indicator’s movable, perpendicular to the test object part. The indicator moves perpendicularly by extending or retreating into its main body.
Contact point
The movement of the plunger will be aided by the point of contact with the surface. As the external pointer completes a full rotation, the smaller pointer will advance from 0 to 1, indicating 1 mm. After the ten revolutions of the larger indicator’s pointer, the smaller one will reset to zero. The readings from the dial gauge’s tiny diameters are incredibly precise and useful.
Stem
The stem is where the plunger or spindle travels up and down.
Types of Dial Indicators
Here are a few types of dial indicators available in the market.
1. Balanced Reading Dial Indicators:
Indicators with a balanced reading dial have information evenly spaced throughout the dial’s face. This dial has numbers printed in two directions, with zero in the middle. It is common to practice displaying positive numbers to the right of zero and negative numbers to the left.
2. Continuous Dial Indicators
In contrast to balanced reading dial indicators, which contain two sets of numbers, continuously numbered dial indicators only have one. The numbers and markings on these dial indicators move in the same direction.
3. Reversed Balance Dial Indicators
Indicators with reversed balanced dials are so called because, although having identical positive and negative scales on either side of zero, the positive numbers are on the left and the negative numbers are on the right.
4. Reversed Continuous Dial Indicators
Dial indicators with numbers that rotate counter-clockwise, also known as reversed continuous dial indicators, are identical to standard continuous dial indicators except that the numbers rotate clockwise.
5. Plunger Dial Indicator
Indicators with a plunger dial have a face similar to a clock’s but are distinguished by the plungers attached to one side. It’s possible to find them in both mechanical and electronic forms.
Plunger dial indicators are often used to check the quality of an injection molding machine. Because of a rack and pinion mechanism, the linear force of the plunger may be converted into a rotary motion for the dial, making this sort of dial indicator functional.
6. Lever Dial Indicators
A lever and scroll mechanism activates the stylus on a lever dial indicator. As a result of its portability and simplicity, dial indicators without plungers are becoming popular.
7. Test Dial Indicators
Test indicators have a dial design similar to a watch’s, but the needle is out to one side. They may be set to precisely the right reading for every piece of equipment you need to gauge.
Working Principle of Dial Indicator
The dial indicator’s plunger, the last part of the instrument, carries a rack in its back and moves over the bearing to make rack-to-pinion contact. The dial indicator’s internals are designed in such a way that the plunger can spin about its axis.
Consequently, operators can secure the accuracy of the measurement by limiting its range with a pin. Operators use the pin as a point of reference by mounting it.
However, a coil spring keeps the plunger in place. The pinion connects the rack and the gear installed on the same spindles; the gear and pinion are mesh to increase the measurement scale. When it happens, the second gear will have engaged the second opinion, and the third pinion will have engaged the second gear and the second pinion. With this step complete, the operator can note the magnification.
Application of Dial Indicators:
- A workpiece can be aligned in a machine with the help of dial indications. In the case of EDM, this includes tools like grinding machines, lathes, and milling machines.
- These tools can also examine a machine tool’s spindle that runs out.
- Dial Indicators provide for precise positioning of workpieces within the spin fixture.
- The roughness of surfaces can also be evaluated with this technique.
- Dial indicators are used to measure parting lines in injection molding.
- It is easy to use dial indicators to determine the height difference between two plates.
- In EDM, a pit depth measurement is a valuable tool.
- Engineers can check the accuracy of a ground piece using a dial indicator.
- In addition, the instruments have effectively aligned a fixture in 5-axis milling machines.
Advantages of Dial Indicators:
- A dial indicator is a highly precise instrument for measuring distances that are only slightly more than a dial indicator.
- A dial indicator is a quick and easy way to measure accurately with minimal effort.
- A dial indicator doesn’t need any special instruction to use.
- Additionally, accuracy is achieved by employing a blade screw, which produces a linear torque proportionate to the angular deflection. Reduces non-linearity, hysteresis, neutral position, and variability-related sensitivity mistakes.
- Because it does not need precise calibration or intricate computations, it can be used by anyone.
- These instruments are far simpler to read than their electronic counterparts, especially in dim lighting. Another possible upside is their low cost compared to other indicator devices like laser or ultrasonic gauges.
Disadvantages of Dial Indicators:
- Dial Indicators frequently lose accuracy due to machine vibration.
- The parallax effect is another major disadvantage of the instrument.
- Since the installation angle reduces the straight-line accuracy of the measuring instrument, it is important to consider the installation angle while planning the installation.
- Dial Indicators can be thwarted by end float. Journal and sleeve bearings both appear to incorporate a little axial play. Because of this, it affects the precision of dial indicators.
Conclusion
A dial indicator is an extremely precise and delicate measuring device that requires special care and storage conditions to maintain accuracy. The dials are pricey because of how sensitive they are.
The mechanical industry relies heavily on it for making instruments of extreme precision. Dial operation also calls for specialized instruction and close monitoring. The Dial Indicator is, at most, one of the most crucial and primary tools you have available.